Food production, specifically agriculture, is a crucial component in the expansion of civilizations. As populations grow, the need for more food rises. The gathering of data is the new frontier in advancement for agriculture technology. The more known about the field the better it can be nurtured. Precision agriculture is defined as “the application of technologies and principles to manage spatial and temporal variability associated with all aspects of agricultural production for the purpose of improving crop performance and environmental quality.” [1].

Another issue that precision agriculture helps solve is disease and pest control. Some diseases are prone to occur at certain combinations of temperature levels, moisture, and too high of PH. A wireless sensor monitoring system can alert the farmer through computer software that a specific region of the field, for example, has PH levels too high and could cause brown rot and suggest appropriate actions are needed.
[1] Francis J. Pierce, Peter Nowak, Aspects of Precision Agriculture, Advances in Agronomy, Volume 67, 1999, Pages 1-85, ISSN 0065-2113
[2] Precision Agriculture Wireless sensor network. Digital image. Source Tech 411. N.p., June 2013. Web.
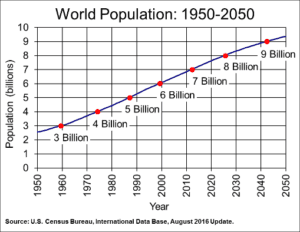
[3] US Census Bureau, Demographic Internet Staff. “International Programs, International Data Base.” World Population: 1950-2050. US Census Bureau, Demographic Internet Staff, 27 June 2011. Web. 29 Apr. 2017.

